

Last updated on

GPT-4 may not be the ultimate solution for SEO automation when compared to Google Cloud’s APIs for text analysis, content transformation, and various other functions.
OpenAI’s APIs, including the large language model (LLM) GPT-4 and its conversational AI, ChatGPT, have garnered significant attention over the past year. Nevertheless, it’s crucial to recognize that established providers like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and AWS have offered marketing APIs for over a decade.
Many SEO professionals, however, have shown a preference for generative AI models when tackling their SEO-related tasks. In this article, we aim to assess and compare the performance of GPT-4 and Google Cloud’s machine learning APIs across common SEO tasks where automation can be effectively applied. These tasks encompass semantic analysis, classification, translation, and image understanding.
While there exist numerous other potential applications of these technologies in the realm of SEO and digital marketing, our primary objectives in this analysis are as follows:
Methodology
To assess the performance of these models, I conducted head-to-head comparisons using identical datasets, which included text, video/audio, or images, depending on the specific task at hand.
For a more comprehensive and robust analysis, I replicated this process across three distinct data points for each task. This approach allows for a more robust and informative “Comparative Analysis” section, where we can draw more accurate conclusions based on multiple data points.
Summary
Here’s a table summarizing the performance analysis:
Understanding text
Named Entity Recognition (NER) stands as a pivotal domain within the realms of computer science and natural language processing (NLP), placing its primary emphasis on the identification and classification of particular entities found within a given text. These entities can encompass a wide range, including but not limited to, individuals’ names, various organizations, and geographical locations.
The primary goal of entity analysis resides in the efficient extraction of such specifics from unstructured textual data, or alternatively, from text characterized by its free-form nature.
In a parallel vein, unstructured text can also undergo scrutiny through the lens of syntax analysis. This discipline is dedicated to comprehending and dissecting the structural aspects of sentences in a given language, thus facilitating the capacity of machines to derive meaning from the presented text.
The fundamental components of syntax analysis encompass the following:
Entity recognition in SEO
In the realm of SEO, the application of entity recognition proves valuable across a variety of projects, including:
By employing entity recognition in these projects, SEO professionals can enhance their understanding of content relevance, user sentiment, and competitor strategies, ultimately optimizing their strategies for improved search engine performance.
Syntax analysis in SEO
In the realm of SEO, text analysis methods prove invaluable when you aim to achieve the following objectives:
By integrating text analysis methods into your SEO strategy, you can effectively navigate the digital landscape, optimize content, and enhance structured data implementation, ultimately driving improved search engine visibility and user engagement.
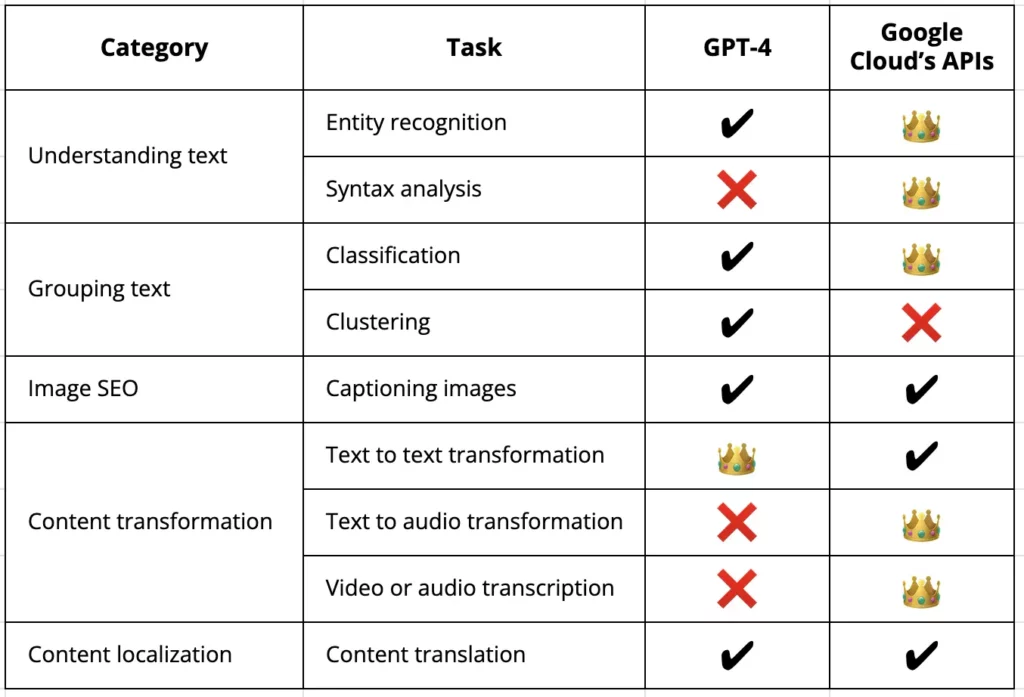
Comparative analysis of GPT-4 vs. Google Cloud Natural Language API on entity extraction and text analysis
Grouping text
In the realm of SEO analysis, two fundamental machine learning approaches, clustering and classification, play pivotal roles in efficiently managing and understanding large volumes of textual data. Let’s explore how these approaches are applied in SEO and why they are crucial:
In summary, classification and clustering are indispensable tools in the SEO toolkit. Classification helps assign predefined labels to data objects, making content management and keyword targeting more efficient. On the other hand, clustering aids in content organization, topic discovery, and user behavior analysis, providing insights that can inform content strategies and improve website optimization efforts. Both approaches enable SEO professionals to make data-driven decisions and enhance their online presence.
Classification in SEO
Explore the following scenarios to grasp the ways in which classification can enhance your SEO strategy efficiency and streamline various processes.
Leverage classification to swiftly identify the diverse range of topics addressed within the website’s content.
Employ classification to assess whether the content on competitors’ websites aligns with your desired business direction.
Clustering in SEO
Explore these real-world applications of clustering in SEO and how it can elevate your strategy and productivity:
Utilizing clustering allows you to categorize and gain insights into the diverse topics present in your keyword dataset.
Topic clusters, based on semantic or keyword extraction methods, can assist in identifying key themes and grouping content together based on their similarity in sub-topics.
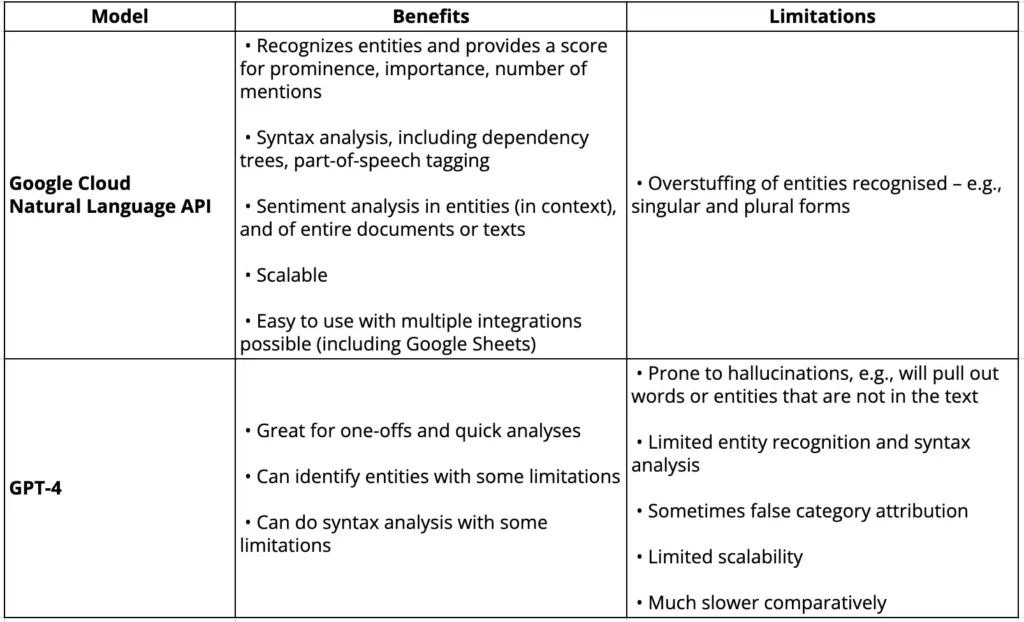
Comparative analysis of GPT-4 vs. Google Cloud Natural Language API on clustering and classification
The table presented below outlines both the advantages and constraints associated with the models that have been examined.
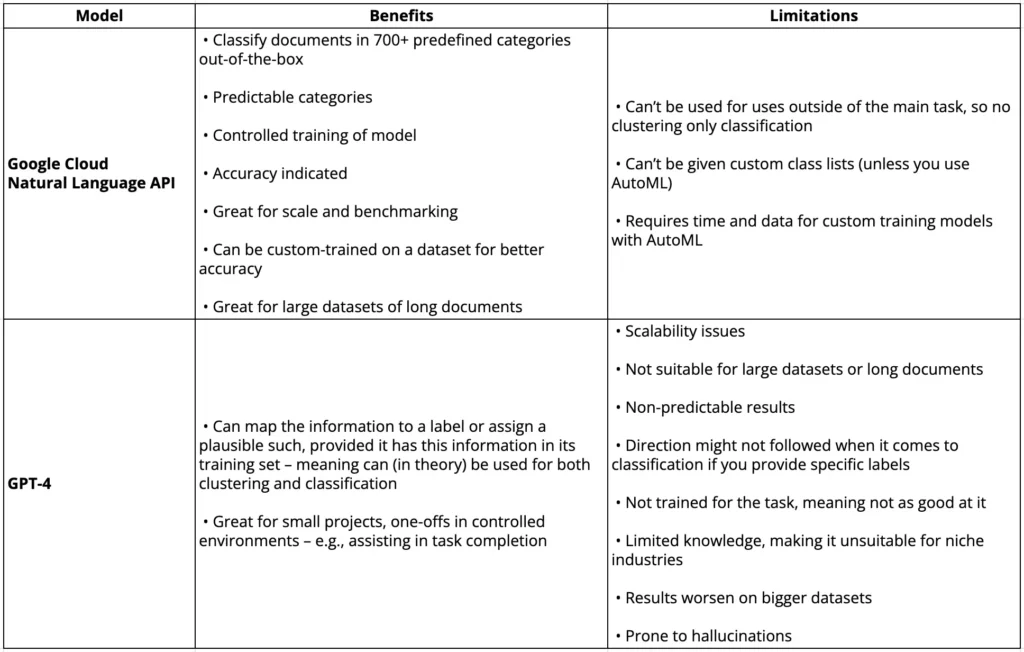
Image SEO
In the realm of image-related tasks, machine learning algorithms can prove to be valuable, particularly in tasks such as image captioning and image generation.
At present, the capability for image generation is exclusively offered by OpenAI’s DALL-E model, without a comparable alternative in Google Cloud.
Image captioning, as one can imagine, holds significant importance in the realm of SEO for various reasons, including:
Comparative analysis of GPT-4V vs. Google Cloud Vision AI on captioning images
In the table below, we compare the image captioning capabilities of Google Cloud’s Vision AI and Vertex AI with the recent addition of GPT-4 with vision capabilities (GPT-4V), accessible through ChatGPT.
One significant factor that may influence your choice between these options is the ease of integrating Google Cloud’s Vertex AI algorithm into a project, allowing you to caption a large volume of images, potentially hundreds or thousands. This can prove exceptionally valuable for enterprises or large websites seeking to meet accessibility requirements. While it’s worth noting that GPT-4’s API endpoint is expected to introduce similar capabilities in the near future, as of now, it has not been implemented, though it may be coming soon.
Content transformation
Content transformation involves converting content into various formats, styles, or lengths. Its significance in SEO can be attributed to two key factors: omnipresence and accessibility.
Omnipresence underscores the necessity for your brand or content to be present across diverse forms and platforms. This need is shaped by:
It’s essential to note that Google does not consider the same content in both written (e.g., a blog) and video formats (e.g., a long YouTube video or shorter clips on Shorts/TikTok) as duplicate content. This approach benefits both users (who can choose their preferred format) and search engines (which can provide content in various formats to meet user search intent).
Accessibility entails offering multiple avenues for individuals to engage with your content, thereby broadening your reach to a more inclusive audience.
Consider different platforms (e.g., YouTube, TikTok, Spotify, Instagram, Pinterest, Medium) and content formats (text, images, video, audio).
For example, transforming textual content into an audio format makes it accessible to individuals with visual impairments and those who prefer listening over reading.
Text-to-text transformation in SEO
To enhance your organic reach, consider employing text-to-text content transformation in the following scenarios:
Text-to-audio transformation in SEO
To enhance your organic reach, consider employing text-to-audio content transformation in the following scenarios:
Video or audio transcription in SEO
Utilizing audio-to-text or video-to-text content transformation can be a valuable strategy to enhance your organic reach in the following scenarios:
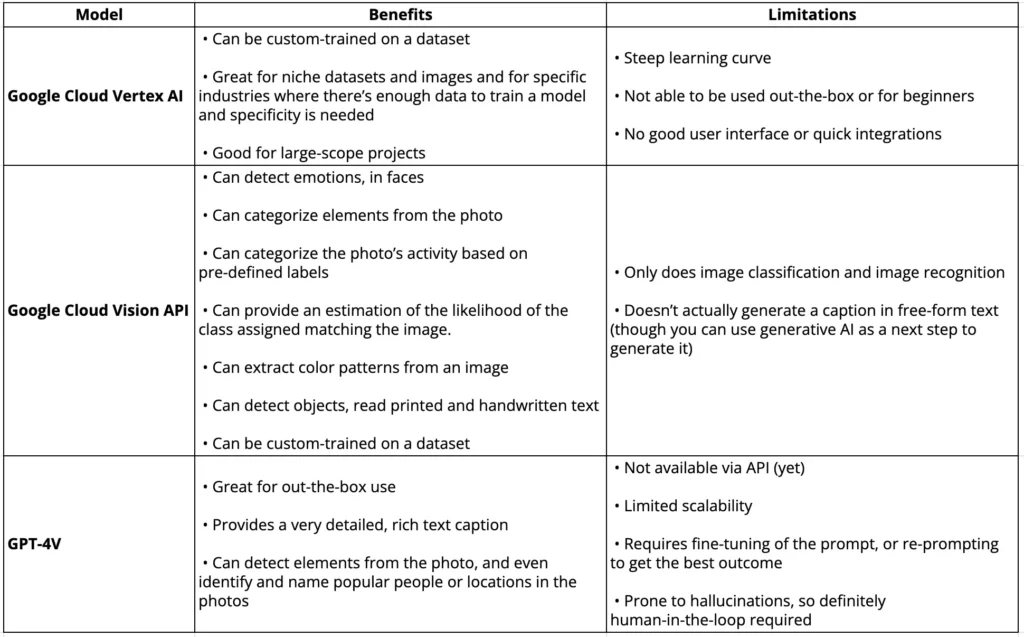
Comparative analysis of GPT-4 vs. Google Cloud on content transformation
The table provided below offers a comparison between three of Google Cloud’s models, depending on the task, and GPT-4’s model. It’s worth noting that the latter doesn’t include built-in text-to-audio or video transcription capabilities; however, these can be integrated using custom agents.
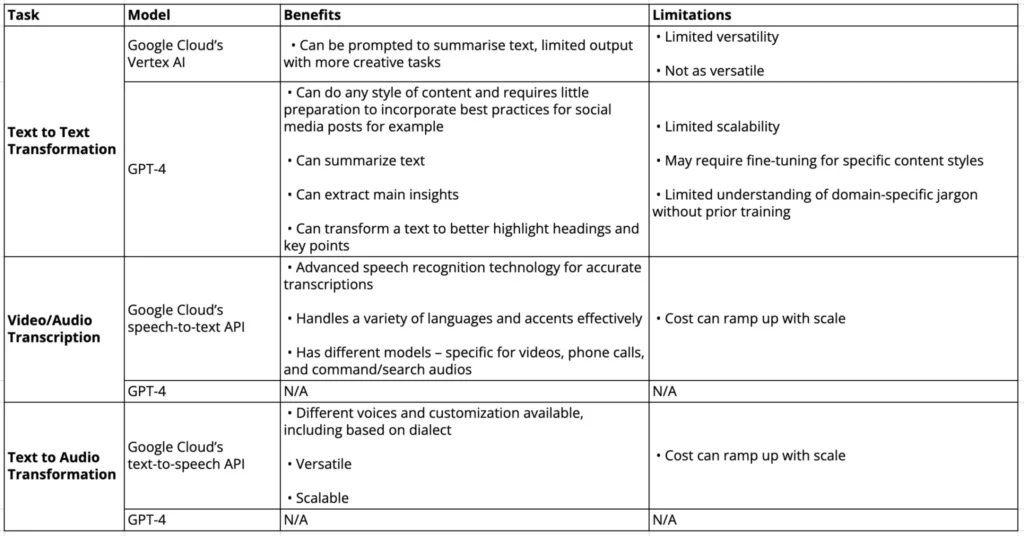
Content localization
Even with the advancements in machine learning models, it’s crucial to understand that translation alone doesn’t fully replace the need for localization, at least not at this point in time.
When dealing with SEO or user-facing content, it’s advisable to have a content localization specialist as the final editor. Ideally, this specialist can also align the last draft of content with SEO research specific to the target market.
Having said that, automated translation can offer significant benefits, particularly for medium and large websites or those working with budget constraints. It’s a faster, more cost-effective, and scalable solution compared to traditional translation methods.
Content translation in SEO
When might you find it necessary to translate your content to enhance your organic search performance? Consider the following potential scenarios:
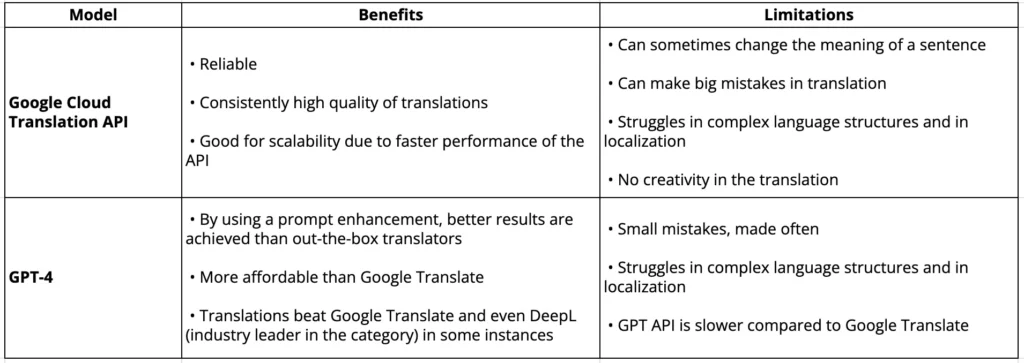
Comparative analysis of GPT-4 vs. Google Cloud Translation AI for content translation
The table below provides a concise summary of the findings obtained through Dmitrii Lukianov’s analysis.
Key takeaway
Rather than relying solely on a one-size-fits-all approach, it’s essential not to overlook the valuable tools offered by Google Cloud, even when you are heavily focused on GPT-4.
I’ve highlighted various tasks where you can leverage these APIs to enhance your strategy, expedite processes, and boost your organic visibility. Utilizing APIs for specific tasks can also have several advantages:
It’s worth noting that each model comes with its unique strengths and limitations for specific tasks. Therefore, thorough research on the capabilities and ideal use cases of each model you employ is crucial before implementation.
Original news from SearchEngineLand